Congenital Heart Disease (CHD): An Overview
Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) refers to structural abnormalities of the heart present from birth. These defects can affect the heart's walls, valves, or blood vessels, leading to disrupted blood flow and impaired cardiac function. The severity of CHD varies; some individuals may experience no symptoms, while others may require immediate medical intervention.
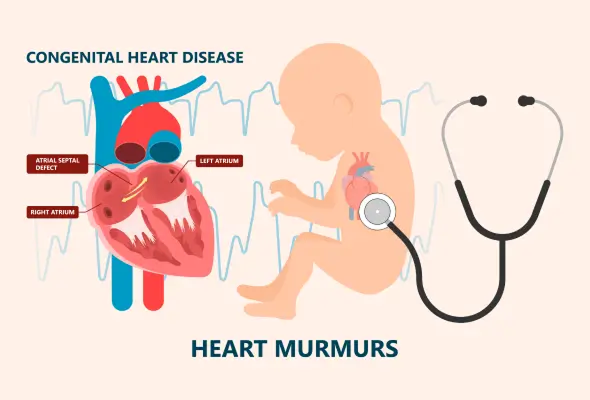
Common Types of Congenital Heart Defects:
Symptoms of CHD:
Government Initiatives for CHD in India:
The Government of India has implemented several schemes to address CHD and other health conditions in children:
Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK): Launched under the National Health Mission, RBSK aims to improve child health by early identification and management of 30 health conditions, including birth defects like CHD. The program targets children from birth to 18 years and provides free treatment, including surgeries for conditions like CHD. Dedicated mobile health teams conduct screenings at Anganwadi centers and schools, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN): This scheme provides financial assistance to patients living below the poverty line who are suffering from major life-threatening diseases, including CHD. The assistance is for treatment at government hospitals with super-specialty facilities. The maximum financial assistance admissible under the scheme is Rs. 15 lakh.
Role of Dhubri Medical College:
As a premier healthcare institution in Assam, Dhubri Medical College is committed to:
For more information or to schedule a screening, please contact the Department of Pediatrics at Dhubri Medical College.